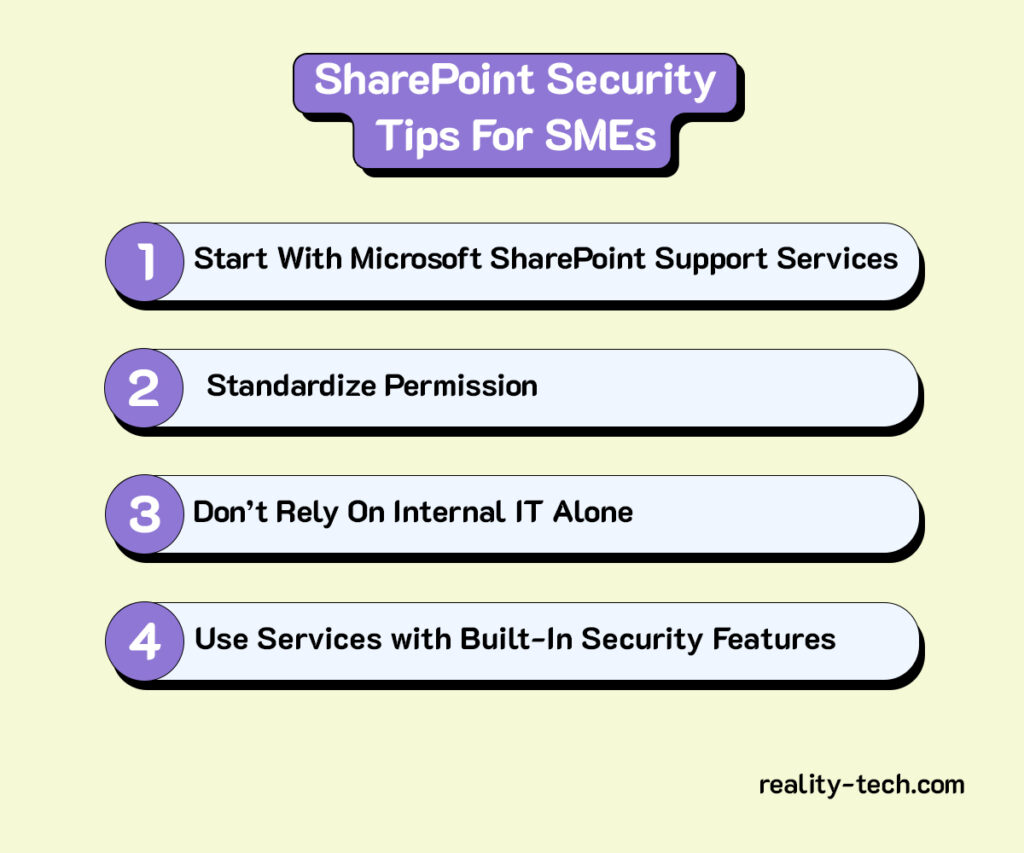
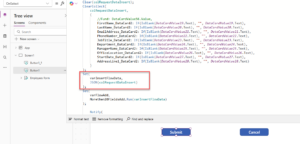
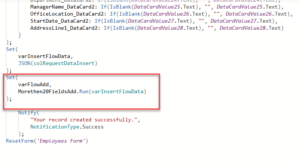
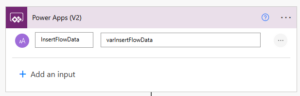
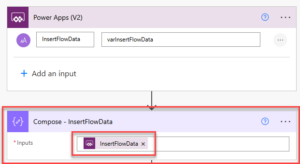
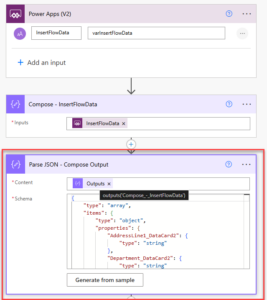
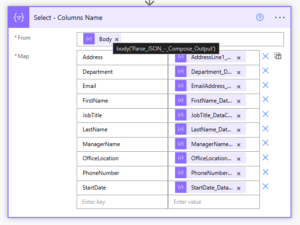
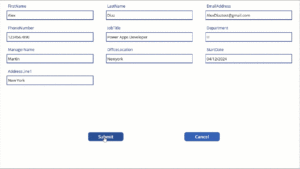
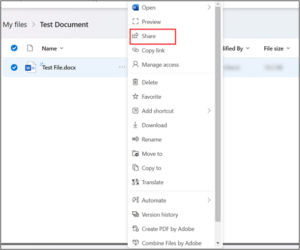
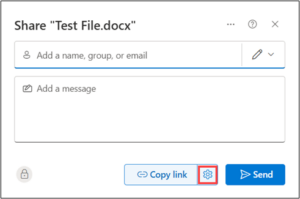
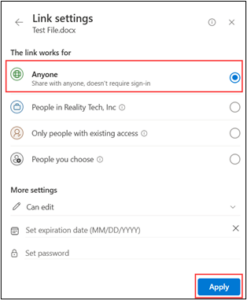
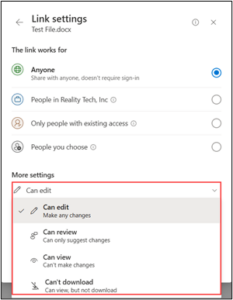
If you’re running a small business, you’re probably wearing multiple hats, handling sales, managing customer support, following up with leads, and juggling invoices. It’s rewarding, but also exhausting.
The good news?
You don’t have to do everything manually anymore. Power Automate workflows can take a load off your shoulders, giving you more time to focus on what really matters.
What is Power Automate?
Let’s be honest, most small business workflows are repetitive and time-consuming. From sending email reminders to updating spreadsheets, these tasks drain your time. Microsoft Power Automate offers a powerful, user-friendly way to automate small business processes without the need for complex coding or IT expertise.
Whether you’re managing a startup or running an established local business, Microsoft Power Automate workflows can streamline your operations, reduce errors, and improve efficiency. You’ll not only save time and money but also boost customer satisfaction by responding faster and working smarter.
Now, let’s dive into the top 10 Power Automate workflows every small business should consider in 2025.
Top 10 Power Automate Workflows for Small Businesses in 2025
Automated Invoice Processing
Tired of manually creating and sending invoices?
Use Power Automate to connect tools like Excel, SharePoint, and Outlook. Automatically generate and email invoices when a deal is closed in your CRM. You can also set up reminders for overdue payments.
Which will save time, improve cash flow, and reduce human error.
Contract and Document Approval Workflow
Route contracts or internal documents for review and approval without manual follow-ups. Automate reminders, track status, and ensure key stakeholders sign off on time, great for legal, HR, or vendor processes.
Collaborating on internal reports or policy updates? Automate the review process, send documents to reviewers, collect feedback, and track versions all in one flow.
This workflow reduces bottlenecks and improves document quality.
Employee Onboarding Workflow
When a new hire joins, trigger a flow that sends welcome emails, sets up accounts, assigns equipment, and shares required documents. Ensures a consistent and professional onboarding experience for every employee or contractor.
Project Status Summary Roll-Up
Managing multiple projects or departments? Use Power Automate to gather weekly updates from different team members and compile them into a single summary report or dashboard.
Perfect for keeping leadership informed without the back-and-forth emails.
Customer Support Ticket Routing
Connect your support inbox or web form to a ticketing system. Based on keyword triggers or categories, route issues to the right person and send an acknowledgment to the customer automatically.
Power Automate for small businesses makes it easier to stay on top of support without needing a large team.
Employee or Contractor Offboarding
When someone leaves your business, Power Automate can help you stay organized, trigger account deactivation, schedule exit interviews, notify IT, and track equipment returns.
This protects your business and ensures nothing is overlooked.
Customer Follow-up Automation
If someone contacts your business or requests a service, you can automatically send a personalized email thanking them and offering next steps or support links.
This small business workflow keeps communication timely and professional, without adding to your to-do list.
Automated Reports and Dashboards
Need to keep tabs on performance? Pull data from Excel, SharePoint, or your CRM and have reports sent to your inbox on a set schedule.
Pair this with Microsoft BI Consulting Services to get meaningful insights without spending hours in spreadsheets.
Lead Capture and Nurturing
Using Microsoft Forms or your website contact form, you can trigger workflows that capture leads, add them to your CRM, and send an introductory email automatically. You can also route high-value leads to your sales team instantly.
You never miss a lead again and engage potential customers while your business is still top-of-mind.
Task Management Integration
Integrate Microsoft To Do, Planner, or Trello with email and calendar systems. Automatically create tasks from flagged emails or calendar events so your action items don’t get lost.
Small business workflow automation like this keeps your team aligned and deadlines on track.
Customer Support Ticket Routing
Connect your support inbox or chatbot to a ticketing system. Based on keyword triggers, route issues to the right department automatically and send confirmation emails to customers.
Power Automate for small businesses makes it easier to manage support queries without needing a full helpdesk team.
Document Approval Process
Need to get contracts or proposals reviewed? Automate the approval process by routing documents to the right team members. Set reminders and track responses to avoid delays.
This will improve accountability and get important documents signed faster.
Automated Reports and Dashboards
Pull data from Excel, SharePoint, or your CRM and send automated reports to your inbox weekly or monthly. Pair this with Microsoft BI Consulting Services to visualize trends and make data-backed decisions.
This is a must-have for business owners who want insights without spending hours on spreadsheets.
How to Get Started with Power Automate Workflows
Now that you’ve seen what’s possible, let’s talk about how to start implementing Power Platform Solutions in your business.
Step 1: Identify Repetitive Tasks
List out tasks you and your team do daily or weekly. Focus on those that are time-consuming, require little decision-making, and happen in multiple apps.
Step 2: Use Power Automate Templates
Power Automate offers hundreds of ready-to-use templates that cover a wide range of use cases, from email automation to file syncing. You don’t have to start from scratch.
Step 3: Connect Your Tools
Power Automate integrates with 500+ apps, including Outlook, Excel, SharePoint, Dropbox, Slack, and Google Drive. Connect the tools you already use to begin automation.
Step 4: Test and Iterate
Run your flows in test mode and adjust based on performance. Start with simple flows and build complexity over time.
Step 5: Get Expert Help If Needed
Sometimes, the best automation ideas get stuck because of technical hurdles. That’s where a Power Automate Consulting Services partner can help.
At Reality Tech, we specialize in helping small and medium-sized businesses harness the full power of Microsoft’s ecosystem. Whether you’re just starting out or want to overhaul outdated systems, we bring years of hands-on experience in Power Platform Solutions, including Power Automate Consulting Services.
We help you build, test, and launch automation flows tailored to your business. Microsoft BI Consulting Services: We turn your business data into visual dashboards that tell stories and uncover trends. End-to-End Workflow Automation: From finance to HR to marketing, we create scalable automation systems that simplify your operations.
Why Now Is the Right Time to Automate
Your competitors are automating, your customers expect faster service, and your team needs more time to focus on meaningful work. Investing in small business workflow automation is no longer a luxury; it’s a necessity.
Whether you’re looking to automate small business processes, improve team productivity, or build smarter systems, Microsoft Power Automate is a tool worth exploring. It’s flexible, scalable, and accessible even if you don’t have a full-time IT department.
By leveraging smart Power Automate workflows, you’re not just saving time, you’re building a more resilient and future-ready business.
Final Thoughts
Small businesses drive innovation, and automation helps you do more with less. With Microsoft Power Automate, you don’t need a big budget or tech team, just the right workflows and mindset.
Start small with one or two simple automations. Watch the impact. Then build from there. And if you need support, expert help is always within reach.
Make 2025 the year you stop working harder and start working smarter.